· Mostapha Benhenda · Articles · 3 min read
FinRL-DeepSeek - new trading AI agents combining Reinforcement Learning with Large Language Models
In algorithmic trading, leveraging unstructured data, like financial news, and managing risk in bear market phases remain challenging.

The world of financial markets is increasingly driven by algorithmic trading, but leveraging unstructured data like financial news and managing risk in bear market phases remain challenging. Our new family of trading agents, FinRL-DeepSeek, address these issues by fusing large language models (LLMs) with risk-sensitive reinforcement learning (RL). Let’s see how this hybrid approach works, and why it matters.
Code, Data and AI agents: Available on GitHub: https://github.com/benstaf/FinRL_DeepSeek.
Current Limitations of Reinforcement Learning in Trading
Most RL-based trading agents focus on price data alone, ignoring alternative signals like news articles. They also struggle with risk management, often failing to mitigate losses during market downturns. Traditional RL algorithms like Proximal Policy Optimization (PPO) prioritize maximizing returns but lack mechanisms to penalize high-risk strategies. This can lead to catastrophic losses in unpredictable markets.
The Solution: LLM-Infused Risk-Sensitive Reinforcement Learning agents
The FinRL-DeepSeek framework introduces two novel components:
LLM-Driven Insights:
- Trading Recommendations: LLMs (DeepSeek V3, Qwen 2.5, Llama 3.3) analyze financial news from the FNSPID dataset (15.7M articles spanning 1999–2023) to generate stock-specific scores (1–5). For example, a score of 5 means “strong buy,” while 1 signals “strong sell.”
- Risk Assessments: A separate LLM prompt evaluates risk levels (1–5) for each stock, identifying high-risk scenarios that might be overlooked by price data alone.
Risk-Sensitive RL Algorithm: The Conditional Value-at-Risk PPO (CPPO) algorithm is modified to incorporate these LLM signals:
- Action Modulation: Trading actions are scaled by recommendation scores. For instance, a “strong buy” (score 5) amplifies positive actions by 10%, while a “strong sell” dampens them by 10%.
- Risk Modulation: Aggregate risk scores adjust rewards in the CPPO objective, penalizing high-risk trajectories.
Key Innovations
- Dual LLM Infusion: Unlike prior work (e.g., FinGPT, FinCon), which uses LLMs for either recommendations or complex multi-agent systems, FinRL-DeepSeek applies LLMs to both actions and risk in a streamlined way.
- CVaR-PPO for Trading: we are the first to adapt CVaR-PPO—a risk-constrained RL algorithm—to stock trading. This encourages the agent optimizes returns while capping losses at a confidence level (e.g., limiting losses to the worst 5% of scenarios).
Results: Beating the Nasdaq Benchmark
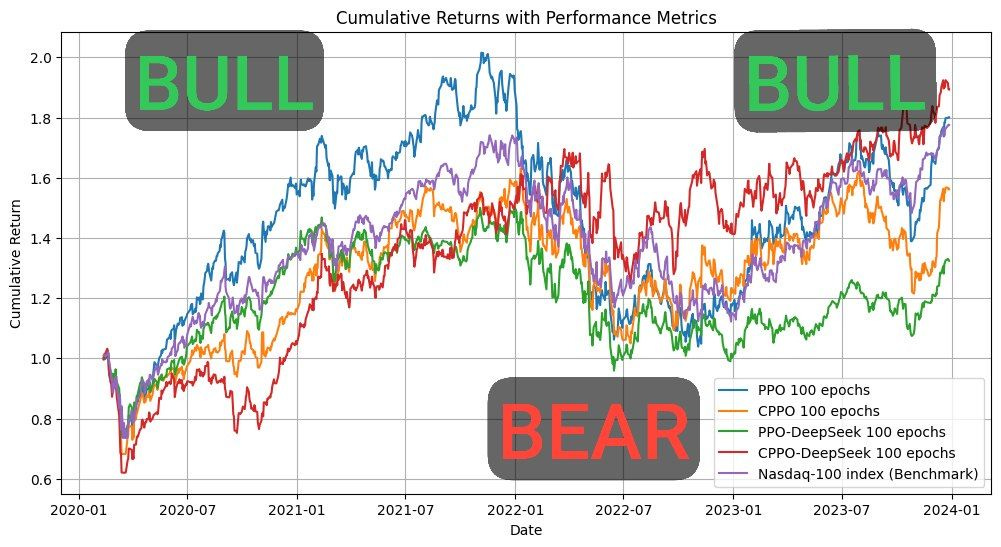
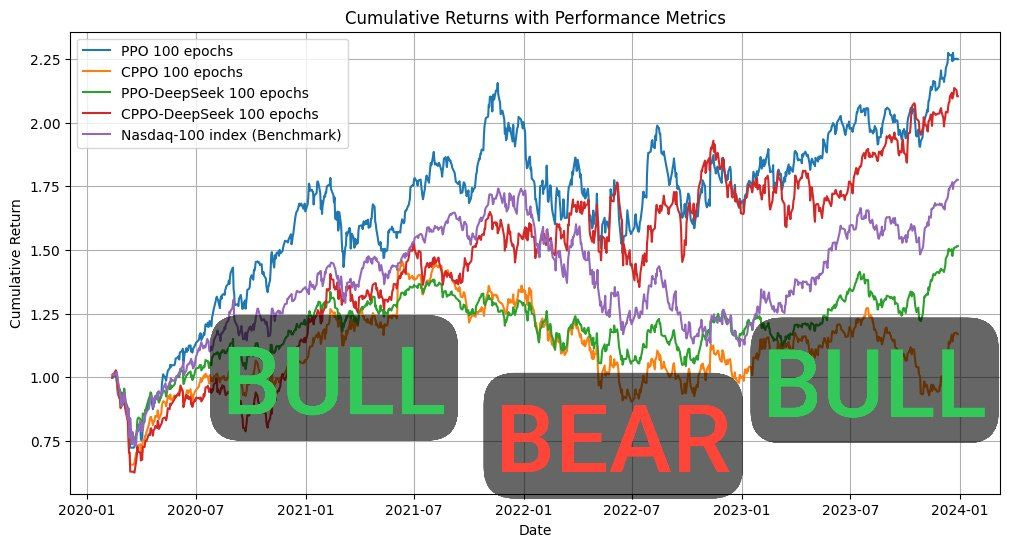
- Risk Adaptation: CPPO-DeepSeek excelled in bear periods, while standard PPO thrived in bull markets. This duality highlights the framework’s ability to adapt to shifting market conditions.
Why This Matters
FinRL-DeepSeek demonstrates that LLMs can do more than sentiment analysis. For quant firms and investors, this approach offers a blueprint for building AI agents that are both data-savvy and risk-aware. As LLMs adoption grows, such hybrid RL-LLM approaches could transform how we navigate financial markets, with many variants remaining to be explored.